Mastering Minnesota’s Building Arena: Your Essential Guide to Contractor Licensing and Thriving in the Construction Industry! Get Your Contractor License In Minnesota.
In Minnesota, the construction industry is a vital component of the state’s economy, contributing significantly to developing and maintaining infrastructure, residential properties, and commercial spaces. At the heart of this bustling sector are the contractors, whose skills, expertise, and professionalism shape the state’s physical landscape. Recognizing the critical role these professionals play, Minnesota strongly emphasizes contractor licensing, ensuring that all individuals and companies engaged in construction work meet stringent standards of quality and safety.<
The state’s approach to contractor licensing is comprehensive, covering various aspects of construction work. Whether it’s a new residential build, a commercial renovation, or a specialized construction project, Minnesota’s licensing requirements are in place to ensure that qualified, knowledgeable, and experienced professionals perform every job. This commitment to excellence enhances the quality of construction projects across the state and fosters consumer confidence and trust in the industry.
For contractor license information in Minnesota, you can contact the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry (DLI).
Contact Information:
Web: Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry
Alternate Phone Number: 512-463-6599 (For calls outside Texas)
Alternate Phone Number: 512-463-6599 (For calls outside Texas)
Phone: 651-284-5005 or 1-800-342-5354
Alternate Phone Number: 512-463-6599 (For calls outside Texas)
Alternate Phone Number: 512-463-6599 (For calls outside Texas)
Address: Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry
443 Lafayette Road N,
St. Paul, MN 55155
For more information, visit: Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry
Who Needs a Contractor License in Minnesota?
In Minnesota, the landscape of the construction industry is diverse, encompassing a wide range of specialties and services. Understanding who needs a contractor’s license in this state is crucial for both contractors and consumers, as it ensures compliance with state regulations and guarantees quality workmanship.
Types of Contractor Licenses in Minnesota
Minnesota’s construction industry is regulated through various types of contractor licenses, each tailored to specific roles and responsibilities within the field. Understanding these license categories is essential for contractors to ensure they operate within the legal framework and for clients to hire appropriately qualified professionals.

General Contractor License:
- Scope: General contractors in Minnesota are licensed to manage and oversee entire construction projects. This includes hiring and supervising subcontractors, ensuring compliance with building codes, and managing project timelines and budgets.
- Criteria: Applicants typically need to demonstrate a combination of education and experience in construction management, pass a state-administered exam, and provide proof of insurance and bonding.

Residential Contractor License:
- Scope: This license is specific to contractors who work on residential buildings, such as houses, townhomes, and small apartment complexes. It covers activities like new construction, remodeling, and repair work.
- Criteria: Similar to general contractors, residential contractors must meet education and experience requirements, pass relevant exams, and carry adequate insurance and bonding.

Specialty Contractor License:
- Scope: Specialty contractors focus on specific areas of construction, such as electrical, plumbing, HVAC, roofing, or landscaping. These licenses are necessary for contractors who exclusively offer these specialized services.
- Criteria: Obtaining a specialty license often requires passing a trade-specific exam, proving a certain level of experience or apprenticeship in the trade, and maintaining trade-specific insurance.

Commercial Contractor License:
- Scope: This license is for contractors who work on commercial projects, including office buildings, retail centers, and industrial facilities. The work often involves larger scale and complexity than residential projects.
- Criteria: Commercial contractors must demonstrate extensive experience in managing commercial projects, comply with specific safety and building codes, and meet higher insurance and bonding requirements.

Home Improvement Contractor License:
- Scope: This category is for contractors specializing in home improvement projects like renovations, additions, and remodeling.
- Criteria: These contractors must show expertise in home improvement work, often requiring a portfolio of completed projects, customer references, and passing a relevant exam.
Application Process for Contractor Licensing
Navigating the application process for a contractor license in Minnesota involves several key steps. This guide provides a comprehensive overview to help applicants understand what is required and how to submit their application successfully.
- Determine the Appropriate License Type:
- Before beginning the application process, determine which type of contractor license suits your needs (e.g., general, residential, specialty, commercial, or home improvement).
- Review the criteria for each license type to ensure you meet the qualifications.
- Gather Necessary Documentation:
- Prepare personal identification documents, such as a driver’s license or state ID.
- Compile proof of relevant experience or education in the construction field.
- Obtain and organize any certificates or results from required trade-specific exams.
- Complete Pre-Licensure Education (If Required):
- Some contractor licenses in Minnesota may require applicants to complete pre-licensure education courses. These courses cover topics like building codes, construction laws, and business management.
- Obtain certificates of completion for these courses to include in your application.
- Obtain Insurance and Bonding:
- Secure general liability insurance and any other required insurance types (e.g., workers’ compensation) as per the license category.
- Acquire a surety bond if required. The bond amount varies depending on the license type.
- Fill Out the Application Form:
- Access the contractor license application form from the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry’s website or a relevant state agency.
- Fill out the form accurately, providing all requested information about your business, experience, and qualifications.
- Pay Application Fees:
- Determine the applicable fees for your chosen license type. These fees vary and are subject to change, so check the latest fee schedule.
- Pay the fees as instructed in the application process. This may be done online or via mail, depending on the system in place.
- Submit the Application:
- Review your application thoroughly to ensure all information is correct and complete.
- Submit the application along with all supporting documents and proof of fee payment to the designated state department.
- Wait for Application Processing:
- After submission, your application will undergo a review process. This may take several weeks.
- Be prepared to provide additional information or clarification if the licensing board requests.
- Receive Your License:
- Once your application is approved, you will receive your contractor license.
- Note the expiration date and any continuing education requirements for future license renewal.
Educational and Experience Requirements for Contractors’ Projects
Obtaining a contractor license in Minnesota requires meeting specific educational and experience prerequisites. These requirements ensure that licensed contractors possess the necessary knowledge and skills to maintain high standards in the construction industry. Here’s a detailed look at what aspiring contractors need to know:

- General Education: High school diploma or GED for foundational knowledge in business and construction.
- Specialized Education: Additional courses in construction management or building science for certain licenses.
- Practical Experience: Varied construction experience, with specific requirements for different licenses.
- Supervisory Role: Experience in managing projects and teams for certain licenses.
- Trade Courses and Apprenticeships: Trade-specific education and hands-on training for specialty licenses.
- Pre-Licensure Education: Courses covering building codes, legal aspects, and business management.
- Continuing Education: Ongoing learning to stay updated with industry changes.
- Documentation: Proof of educational and professional experience is required for application.
Insurance and Bonding Requirements for Minnesota Contractors
Contractors in Minnesota must meet specific insurance and bonding requirements as part of their licensing process. These requirements are designed to protect both the contractor and their clients from potential financial losses due to accidents, damages, or failures to fulfill contractual obligations. Here’s a detailed overview of what contractors need to know:
- General Liability Insurance:
- Purpose: This insurance covers claims of bodily injury, property damage, and personal injury that might occur during construction activities.
- Coverage Limits: The required coverage limits can vary based on the contractor’s size and the nature of their projects. Contractors should consult with an insurance professional to determine the appropriate coverage amount.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance:
- Applicability: This is mandatory for contractors who have employees. It covers medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and lost wages for employees injured on the job.
- Exemptions: Sole proprietors or independent contractors without employees may not be required to carry workers’ compensation insurance, but they should verify this with the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry.
- Professional Liability Insurance (Errors and Omissions):
- Relevance: While not always a legal requirement, this insurance is crucial for contractors offering design or consulting services. It protects against claims of negligence or failure to perform professional duties.
- Coverage Details: The policy should cover legal defense costs and settlements or judgments.
- Surety Bonds:
- Function: A surety bond is a financial guarantee that the contractor will comply with contractual and regulatory obligations. If the contractor fails to meet these obligations, the bond can provide compensation to the client or the state.
- Bond Amounts: The required bond amount varies depending on the contractor’s license type and the scope of their work. Contractors should check with the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry for specific bond requirements.
- Vehicle and Equipment Insurance:
- Necessity: For contractors using vehicles and heavy equipment, this insurance is essential to cover damages or accidents involving these assets.
- Coverage Scope: Policies should cover both liability and physical damage to vehicles and equipment.
- Umbrella or Excess Liability Insurance:
- Additional Coverage: This type of insurance provides extra liability coverage above the limits of the contractor’s other policies.
- Consideration: It’s particularly useful for contractors working on large-scale or high-risk projects.
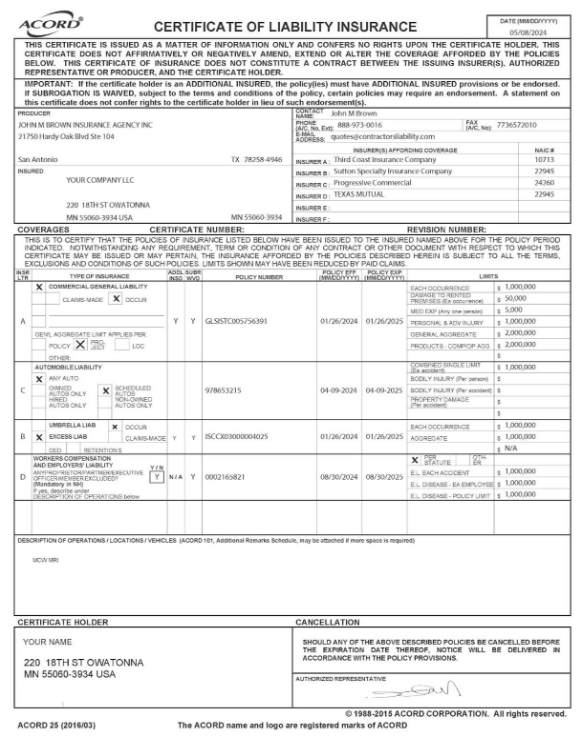
- Documentation and Proof of Insurance:
- Submission to Authorities: Contractors must submit proof of insurance and bonding to the relevant Minnesota state authorities as part of the licensing process.
- Client Assurance: Providing proof of insurance to clients can also be a sign of professionalism and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
These are common questions about General Contractor License in Minnesota.
Minnesota offers various contractor licenses, including general contractor, residential contractor, and specialty contractor licenses. Each has its own scope and criteria.
Yes, most contractors, especially those working on residential buildings or specific specialty areas, need to be licensed in Minnesota.
The educational requirements vary based on the type of license. Some may require completion of specific courses or apprenticeship programs.
You can apply through the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry. The process involves submitting an application along with required documents and fees.
Contractors typically need general liability insurance, workers’ compensation insurance (if they have employees), and a surety bond. The exact requirements and amounts vary.